[Update 2023]: The Steps mentioned in this post is also applicable for the latest versions Pentaho Data Integration (version 8, 9 and above).
Let us assume, we have an transformation with simple data set having population count of states in India city wise. We need to get the total population count. We build a simple transformation file using Memory Group By Step and group the source data on the basis of State to get the total population count.
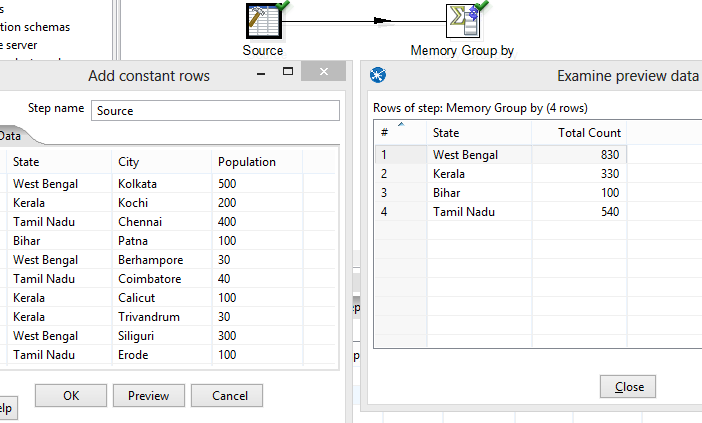
Now, suppose instead of having small set of source data, you are having millions of records coming in from your source. So Memory group by step will cost you huge. Instead of simply passing by, we leverage on the power of the multi-core machines.
Pentaho provides you will an option to define the Number of copies of data in the step. Defining multiple rows of Memory Group By Step in Pentaho is one way of using the multi-core machines. So lets do the following to the Memory Group By Step:
- Right Click on Memory Group By
- Select Change number of copies to start
- Give the Value as 3 or any number greater than 1
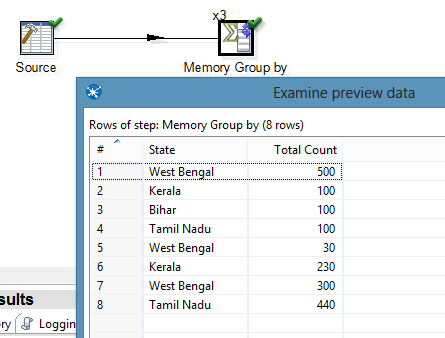
But once you execute the above transformation, we see that the results are very different and is not what is expected. This is because, the source step is sending the data in Round-robin fashion to 3 copies of Memory Group by step. Each of these Memory Group by step process the data in its own manner and finally sends out the output. This is parallelism in PDI but in this case we are not getting the correct output.
So what we do here is to Partition the data. The idea here is to send the similar sort of data to each of the partition and then do the group by instead of grouping as per the above data. Its like 3 Memory Group by Step each having partition data like West Bengal in Partition 1, Kerala in Partition 2, etc.

Steps to follow to create a partition:

Subscribe to continue reading
Subscribe to get access to the rest of this post and other subscriber-only content.

