Introduction
On May 18, 2021 at Google I/O 2021, Google Cloud announced the first general availability of Vertex AI, a unified AI/ML platform that allows companies and developers to accelerate the development and maintenance of AI/ML solutions. So what exactly is it and why we need to be (or not to be) excited about it.
Vertex AI
We had two guiding lights while building Vertex AI: get data scientists and engineers out of the orchestration weeds, and create an industry-wide shift that would make everyone get serious about moving AI out of pilot purgatory and into full-scale production
Andrew Moore, vice president and general manager of Cloud AI and Industry Solutions at Google Cloud
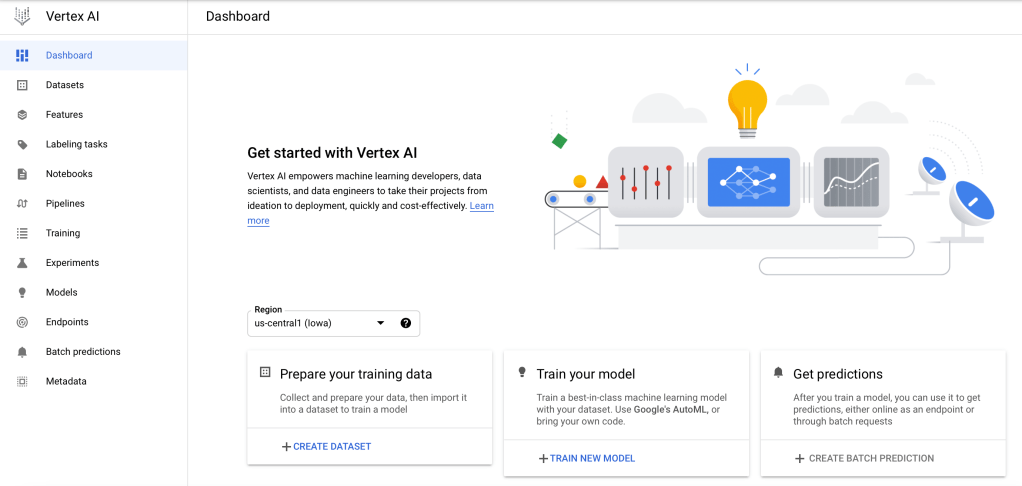
Vertex AI is a managed machine learning (ML) platform that allows companies to accelerate the deployment and maintenance of artificial intelligence (AI) models.
According to Google, Vertex AI requires nearly 80% fewer lines of code to train a model versus competitive platforms, enabling data scientists and ML engineers across all levels of expertise the ability to implement MLOps to efficiently build and manage ML projects throughout the entire development lifecycle.
Why there is a need?
Common building construct of any machine learning frameworks today consists of:
Data Extraction
Extraction of data using standard ETL or ELT tools or services and storing them in an object storage or any database for further analysis.
Data Analysis, Preparation and Cleaning
Once the data is stored on cloud, a standard process of analysing the data and also transforming the data comes into play. This process can either be carried out by using standard ETL/ELT tools or using cloud services.
Model Training
Once the data is cleaned and transformed, Data scientists train the model using a bunch of ML algorithms. The algorithms can be either Custom models or AutoML depending on the dataset processed and stored in the previous steps.
Model Evaluation and Tuning
Upon training, models are evaluation for prediction accuracy and bias. This is a continuous process of development and requires to train the model again to achieve a desired result.
Model Deployment
Once the model are trained and evaluated, it is deployed on a scalable infrastructure with endpoints exposed.
Model Prediction and Monitoring
A critical step is to monitor the performance of the models on live dataset. Based on the accuracy rate of the prediction, the models are retrained and the entire process starting from model training till monitoring are carried out.
Having said that, the above pipeline stages are quite significantly different to each others. Depending on how you do your ETL, rest of the pipeline becomes quite different. For e.g. tabular CSV dataset ML pipeline execution is quite different than an image classification one. The storage location and type of your dataset is also a big factor e.g. store in local SSD disk or on Cloud Storage. Hence there is a need to have a unified definition of data.

Subscribe to continue reading
Subscribe to get access to the rest of this post and other subscriber-only content.