- ⏩ TL;DR
- 🚀 Introduction
- 📖 Understanding Data Lineage further
- 🏦 Solving Data Lineage for Enterprises
- ⭐ Recommended Reads
⏩ TL;DR
- Data lineage tracks data from its origin to destination, crucial for data management and governance frameworks, benefiting data engineers and owners by ensuring quality control and compliance.
- While data provenance focuses on the origin and history of data, data lineage provides a broader view, detailing its journey through processes and transformations.
- Data lineage can be table-level or field-level, with techniques including inferred lineage, tagging, self-contained lineage, and factual lineage, each with its advantages and limitations.
- Various tools like Solidatus, Alation, Pentaho Data Catalog, and Monte Carlo offer data lineage solutions, with factors to consider including data source integrations, column-level lineage support, adherence to standards like OpenLineage, visualisation capabilities, and security measures.
- Enterprises face challenges in implementing robust data lineage due to complex ecosystems, inadequate governance, lack of expertise, and overemphasis on tools. Strategies for building data lineage include metadata management maturity, tool evaluation, education and awareness, and iterative scaling.
🚀 Introduction
Data Lineage
Data lineage refers to the end-to-end view of the flow of data from its source (origin) through various processes and transformations to its target (destination). It traces the lifecycle of data, detailing how it is created, manipulated, utilised and accessed within a system or across systems. Building and understanding the lineage of your data is a critical part of the data engineering and analytics projects, impacting both the engineering and the business side of your projects.
Data Lineage is one of the key component of the overall Data Management and Governance frameworks. The primary audience of data lineage are the data engineers and data owners who need to monitor and keep the quality control on their datasets.
The need for data lineage
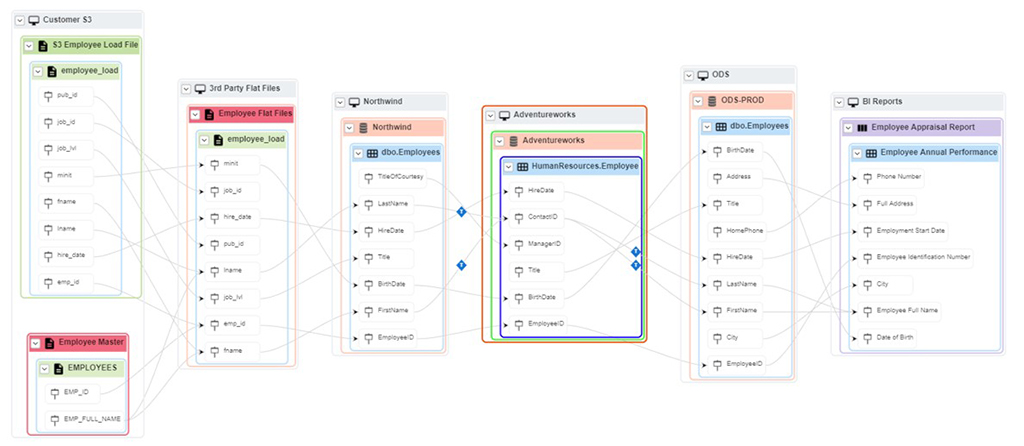
With the increase in data usage, data regulations (GDPR), AI and others, understanding and trusting the source of your data is of the highest demand. Data engineering teams having large scale projects struggle to understand and figure out the source of their data. It becomes a difficult task to understand some of the legacy systems codes and align with the business rules and definitions. Data lineage is crucial for understanding the provenance of data, ensuring data quality, compliance with regulations, and troubleshooting issues within data pipelines or workflows.
In summary, Data lineage allows enterprises to:
- Identifying data quality issues: Data lineage provides transparency into the flow of data, allowing organisations to identify potential issues such as data inconsistencies, inaccuracies, or anomalies. By understanding the origin and transformations applied to data, organisations can implement quality control measures to ensure data accuracy and reliability.
- Enabling effective data governance: It supports effective data governance by providing visibility into data assets, their usage, and lineage relationships. It helps organisations establish data ownership, define data policies, and enforce data quality standards.
- Regulatory compliance: Many industries are subject to regulatory requirements regarding data management and reporting. Data lineage helps organisations demonstrate compliance by providing a comprehensive audit trail of data movement and transformations. This enables organisations to track data lineage for regulatory reporting, such as compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, or financial regulations.
- Impact analysis: Data lineage enables organisations to assess the impact of changes to data sources, processes, or systems. By understanding how changes propagate through data pipelines, organisations can anticipate potential impacts on downstream systems or analyses. This helps mitigate risks and ensures business continuity during system upgrades, migrations, or changes to data schemas.
- Troubleshooting and RCA: When data issues arise, such as discrepancies or errors in reports or analyses, data lineage serves as a valuable tool for troubleshooting and root cause analysis.
Data Provenance
You may have come across the word Data Provenance in the sales, marketing slides or in a data governance meeting. Hence, it has become necessary to talk briefly about data provenance.
In short, Data Provenance refers to the history and origin of data, including its creation, movement, and transformations throughout its lifecycle. Unlike a data lineage, data provenance looks into the metadata of source data, providing authenticity and historical context.
Difference between Data provenance & Data lineage
| Category | Data Provenance | Data Lineage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Primarily emphasises the origin of data and its history. It involves tracing the lineage of data back to its creation point, documenting the processes it has undergone, and identifying any transformations or modifications it has experienced | It is a broader concept that encompasses not only the origin of data but also its entire journey through various processes and transformations. It involves documenting the flow of data from its source through different systems, applications, and transformations to its final destination. |
| Solves concerns | What source this data comes from? Who changed the data source? Who created the data source? | Where is this data coming? Who is using this data? What happened to this table? |
| Key Target Audience | Data Analysts, Data Owners | Data Engineering, Data Stewards |
📖 Understanding Data Lineage further
Data Lineage types
In practise, data lineage are basically of two types:
Table-Level Lineage
This is a high level view of the end to end lineage. Table level lineage illustrates how multiple tables are connected with other tables in a data environment. This type of lineage however fails to cover the origin details of the table.
Field-Level Lineage
The field level lineage looks at the individual column level information from source to target datasets. It is useful for data observability use-cases and enable data engineers to quickly identify and trace the issues in the data pipeline at an object field level.
Data lineage generation techniques
For a data engineering mind, the real question is how to generate data lineage of their organisation’s data pipeline. There are many products in the market that provide out of the box data lineage solutions. However, there is no one-solution-fit-all method to view the data lineage. Some of the techniques or methods that products usually take are as follows:
Inferred Lineage
This technique of generating lineage is also refereed as the automated lineage or Pattern based lineage. Lineage is generated based on the automated matching of the similar data or metadata of two database objects. For example: if two tables contain columns (fields) with similar data and metadata (datatypes, cardinality, etc.), it is highly likely to have a matching relationship.
The advantage of using this technique is its product agnostic capability. Since the reliability is on matching the data and the metadata, this process doesn’t have to rely on specific version of the databases (Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc.).
The key disadvantage with this approach are the incorrect mappings. Inferred lineage are not always accurate as they either miss to identify relationships between fields due to some transformation logic or they may incorrectly match them. Hence, the reliability of such approaches diminishes in the real-world scenarios.
Lineage by Tagging
As the name suggests, the Lineage by Tagging approach is dependent on reading the tags from the data pipeline. This approach traces and queries the tags from the start to the end of the data pipeline.
This approach is suitable for closed data pipelines systems where tagging of the ETL workflow can be achieved easily. Such processes require a deep understanding of the pipelines and struggles to generalise against a plethora of ETL products in the market like Pentaho, Informatica, Talend, etc.
Self-contained Lineage
Another approach of generating lineage is by reading the metadata stored in the data stores (database, object store, etc.). This approach is applicable for data engineering projects that maintain every metadata about their data pipelines. However, similar to the above technique, self-contained lineage approach is suitable for closed systems. They are not open and fails to generalise against the other systems.
Factual Lineage
Factual lineage or lineage by parsing is the method to generate lineage by parsing the data pipeline code. These include applying custom algorithms to parse the SQL queries, read ETL logs, etc. to generate the lineage. It generates the most accurate picture of the lineage.
The advantage of using factual lineage is the accuracy of the generated lineage. Once implemented, factual lineage can be re-used across other domains of the organisations as the parsing queries and logs are standard across the community. The key disadvantage is the complexity of this approach. Factual lineage can become quite complex to implement and enterprises require specialised skills and efforts to develop a generalised lineage solutions.
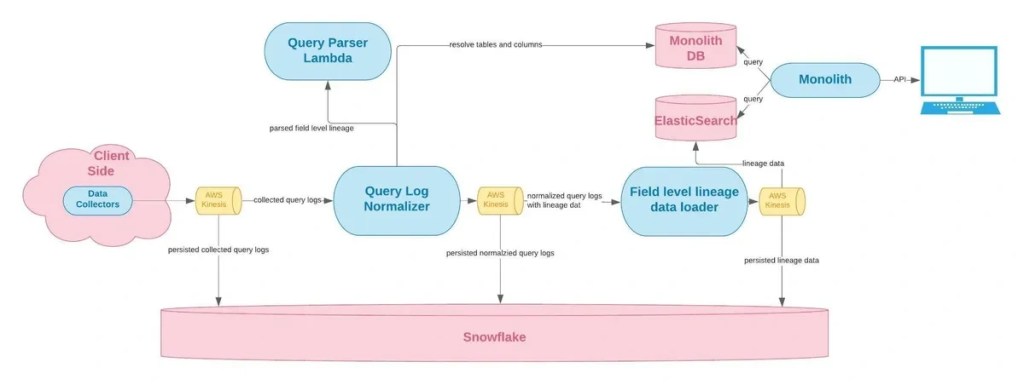
One example of end-to-end factual lineage solution (above diagram) is provided by Monte Carlo’s team. At a high level the approach looks into collecting SQL queries, parsing and generating the field level lineage. The solution involves using various technologies like AWS services like Kinesis, Snowflake, ANTLR, Elastic Search and PostgreSQL as metadata store. The solution approach is a custom solution and supports parsing of databases like Presto, Redshift, Snowflake, and BigQuery.
Having said that, most of the enterprises require a custom solution for their needs involving parsing complex ETL pipelines, SQL queries and other codes. Data Catalog products like Pentaho Data Catalog along with its professional services team supports the generation of the factual lineage.
Data lineage tools in the market

There are a catalogue of tools in the market that support data lineage. Some of them are provided as below:
- Solidatus
- Alation
- Pentaho Data Catalog (previously Lumada data catalog)
- Collibra
- Monte Carlo
- Informatica Metadata Manager
- IBM Infosphere Information Governance Catalog
- Atlan
- MANTA
- Apache Atlas
🏦 Solving Data Lineage for Enterprises
Why Enterprises are failing to leverage data lineage?

Subscribe to continue reading
Subscribe to get access to the rest of this post and other subscriber-only content.